USC's Cryo-EM Instruments
USC has two cryo-electron microscopes available for use: Krios with the K3 direct detection camera and Glacios with the Falcon 4 direct detection camera, both manufactured by Thermo Fisher. Both instruments are housed in the Michelson Center for Convergent Bioscience building in the Core Center for Excellence in Nano Imaging (CNI) at USC’s University Park campus.
This user guide explains how to get started using the new microscopes, including setting up your cryo-EM project and allocations in the CARC user portal, reserving the microscopes using CNI’s reservation system, configuring the data acquisition process and pre-processing parameters, accessing the microscope data, and analyzing the data.
1 Creating a cryo-EM project in the CARC user portal
To use the cryo-EM instruments, you must have a project and associated resource allocations in the CARC user portal. Create a new project for your cryo-EM work or add the required resource allocations to an existing project.
The cryo-EM project needs the following allocations:
- Cryo-EM subscription allocation
- Project2 storage allocation (Check here for the details)
- Discovery cluster allocation
See the Request a New Allocation user guide for detailed instructions for requesting allocations for your project. The allocations should be approved by CARC staff within 24 hours.
The resources enabled by the cryo-EM subscription allocation are:
- Access to the cryo-EM pre-processing portal, where you can get live feedback during the data acquisition process
- GPU cluster with 10 GPU compute nodes
- Access to the temporary cryo-EM storage space (
/cryoem2) for the datasets collected by the microscopes. This storage option functions as a parking zone for raw data obtained from USC’s cryo-electron microscopes. There is no fee for parking raw data on /cryoem2, but the data can only be kept there for a limited time before it needs to be transferred to /project2 or another storage system. CARC only guarantees the datasets for two weeks after the final set of data has been acquired. More details on /cryoem2. You can learn more about transferring data to your personal CARC directories (or elsewhere) in our Transferring Research Data user guide.
2 Reserving a microscope
To reserve time to use the microscopes, you must submit a request through CNI’s reservation system click here.
Use of the microscopes is a paid service—pricing details can be found here.
3 Using the microscope
When your reservation time begins, log in to the CNI client on the microscope’s support PC, and use the microscope’s control PC to configure the data acquisition process for the microscope you’re using.
#Important: Make absolutely sure that you follow the file naming scheme below or your data will not be transferred from the microscope.
The data acquisition protocol is similar for both microscopes:
→ Data acquisition protocol for Krios
- Open EPU program on control PC
- Create a new session
- Give the session a name of the form
YYYYMMDD_USC_<USC NetID of the user>_<Cryo-EM project ID>_k3_<sample_name> - Change storage directory to X
- Change file type to TIFF (not MRC)
- Proceed to grid square and hole selection
- Execute the template
- Open the web application to initiate the cryo-Pegasus process
→ Data acquisition protocol for Glacios
- Open EPU program on control PC
- Create a new session
- Give the session a name of the form
YYYYMMDD_USC_<USC NetID of the user>_<Cryo-EM project ID>_f4_<sample_name> - Change storage directory to M:
- Change file type to TIFF (EER also works but is slower due to the technicality of this file format)
- Proceed to grid square and hole selection
- Copy gain reference to the session directory on M:\
YYYYMMDD_USC_<USC NetID of the user>_<Cryo-EM project ID>_f4_<sample_name> - Execute the template
- Open the web application to initiate the cryo-Pegasus process
After setting up the data acquisition process for the microscope, log in to the CARC cryo-EM user portal in a web browser and navigate to the Instrument CheckOut/Return page:
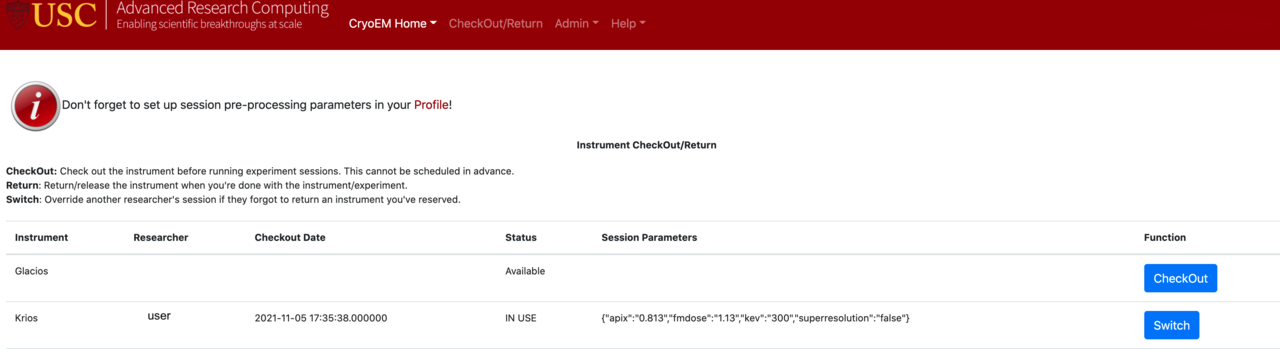
Click the blue CheckOut button for the microscope you reserved and set the following pre-processing parameters:
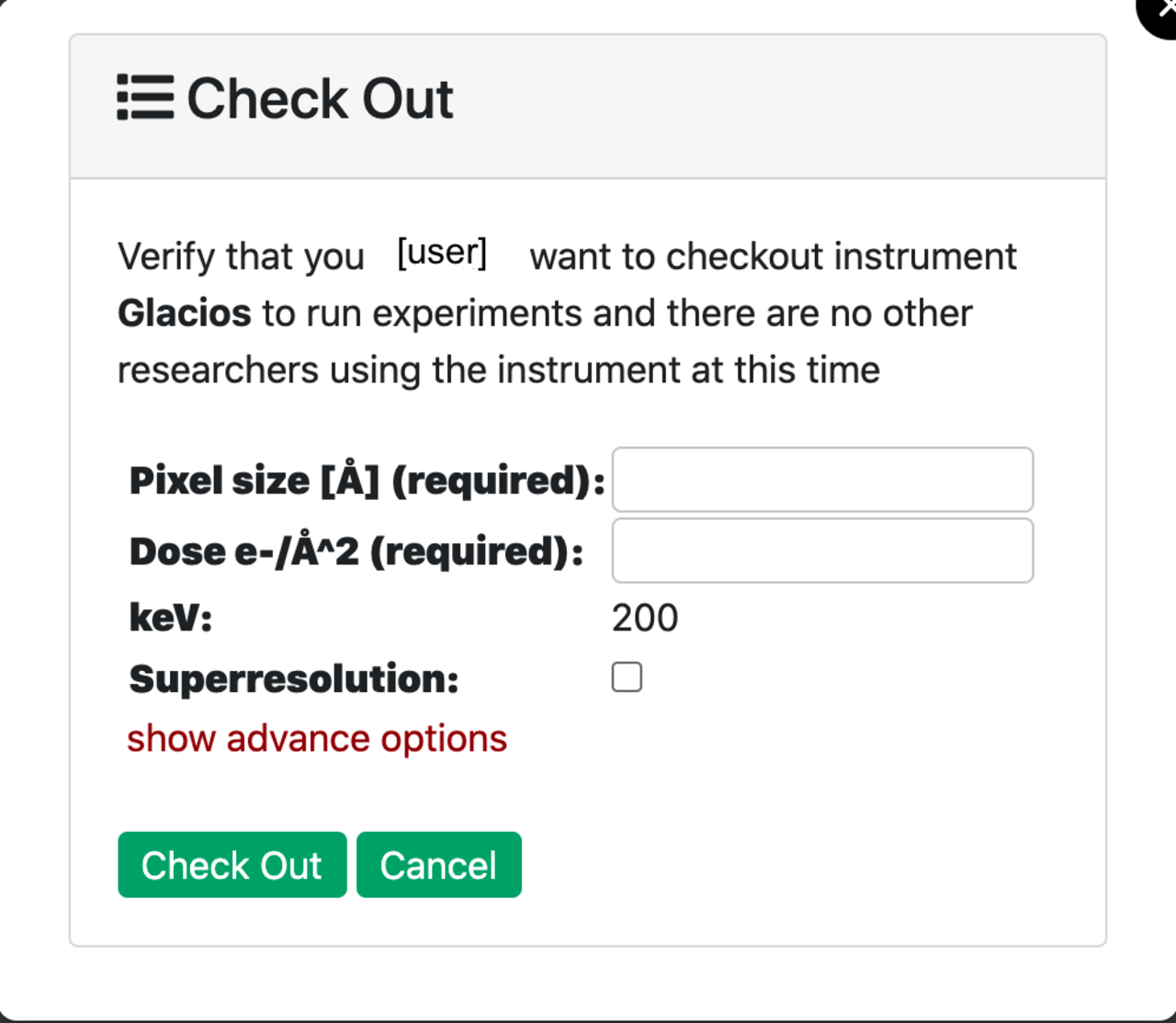
- Project_ID: choose a project you are a member of to use with the Cryo-EM processing.
- Pixel size: Determined during data acquisition setup. Usually between 0.6 and 1.1.
- Dose of electrons per Angstrom square per frame (Dose e-/Å^2): Determined during data acquisition setup. Usually it is about 50 electrons per 40 frames.
- keV: 300 for Krios, 200 for Glacios.
These parameters will be used by the Cryo-pegasus data pre-processing workflow powered by Pegasus, a workflow management system.
Once the microscope has been checked out with the pre-processing parameters set, the transfer and processing of data from the microscope will be automated. If this is your first time using the microscopes, you will be added to a Slack workspace called USC CARC cryo-EM. You will then be added to a private Slack channel dedicated to the microscope session you just created where you will be able to view the pre-processed images from the microscope as they are transferred, with every image labeled with its potential (R)esolution, (A)stigmatism and the average (S)hifts:
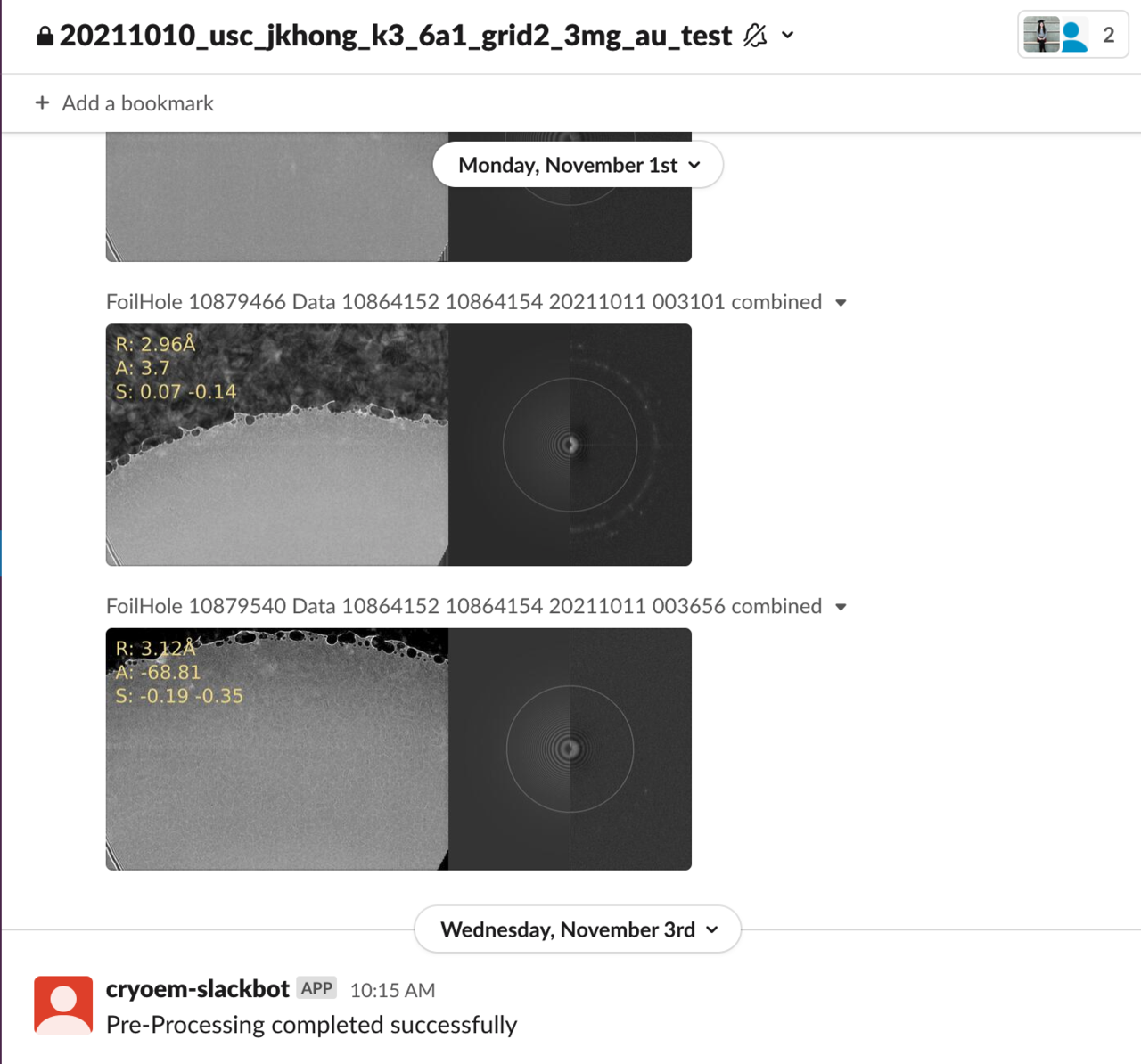
Data should begin flowing from the microscope in about ten minutes.
When you are finished using the microscope, you should to “return it” in the CARC user portal using the Instrument CheckOut/Return page. This makes it available for the next user to check out. You can also use the “Switch” option to override another user’s session if they forgot to return an instrument you’ve reserved.
4 Accessing your data
Data from the microscope will be saved within your project directory in the cryo-EM shared file system (/cryoem2) in a subdirectory with a name of the form YYYYMMDD_USC_<USC NetID of the user>_<Cryo-EM project ID>_<detector>_<sample_name> (e.g., 20230801_USC_ttrojan_ttrojan_k3_mysample). The data in this subdirectory will include the raw data as well as the processed images.
This subdirectory in /cryoem2 is different from your main /project2 directory in the CARC /project2 file system.
Access the cryoem2 file system by logging in to the cryo-EM login node (knoll.usc.edu), which is set to be accessible the same way as other CARC login nodes.
ssh <username>@knoll.usc.eduMake sure to substitute your USC NetID as the username. This is the same username for your USC email account (e.g., ttrojan@usc.edu’s NetID is ttrojan). After entering the command, you will then be prompted to enter your USC NetID password. This is the same password for your USC email account.
There will be no visual feedback as you enter your password. This is a security feature designed to obscure your password and is expected.
After entering your password, you will then see a Duo two-factor authentication prompt. You can learn more about transferring data from cryoem2 to your personal CARC directories (or elsewhere) in our Transferring Research Data user guide.
5 Analyzing your data
CARC provides access to a managed instance of cryoSPARC processing software, which supports fast and convenient dataset analysis and 3D reconstruction. Moreover, with the use of cryoSPARC Live, you can process your data and observe results in real time. To request access to cryoSPARC, please contact us by submitting a help ticket.
Accessing cryoSPARC requires the use of the USC Wi-Fi or a USC VPN; see the Connecting to a USC VPN guide for instructions.
Cryosparc
Relion
The team running the Biowulf cluster at NIH provides an in-depth guide to use Relion on a cluster with slurm. After a minimal adjustments for resources available at CARC it can be used to prepare and successfully run jobs. Feel free to reach out to us by submitting a ticket if you need any additional help or guidance.
CARC also provides a range of cryo-EM data processing software on the Discovery and Endeavour clusters:
- Relion: A software package that employs an empirical Bayesian approach for cryo-EM structure determination.
- MotionCor2: Correction of electron beam-induced sample motion.
- ctffind4: A fast program for finding the Contrast Transfer Functions of electron micrographs (CPU only version).
- pyEM: A selection of Python programs for cryo-EM.
- EMAN2: A broadly based greyscale scientific image processing suite with a primary focus on processing data from transmission electron microscopes.
- IMOD: A set of image processing, modeling, and display programs used for tomographic reconstruction and for 3D reconstruction of EM serial sections and optical sections.